General Treatment
Crowns
Implants
Bridges
Fillings
Extractions
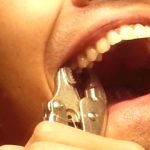
Wisdom Teeth
In certain cases, the wisdom tooth that cannot come through becomes inflamed under the gums and in the jawbone, causing a sac to develop around the root of the tooth that then fills with liquid. This can cause a cyst or an abscess if it becomes infected. If either of these situations goes untreated, serious damage to the underlying bone and surrounding teeth and tissues can result.
To potentially stave off this result, an extraction of one, several or all of the wisdom teeth may be advised. If that is the case, we have the equipment and training needed to perform such extractions, with an absolute minimum of discomfort. Ask our staff for more information regarding tooth extractions if you feel you may need one.
Root Canals
A cavity is the result of superficial decay of the enamel of the tooth. Left long enough, this decay can burrow into the deeper reaches of the tooth, causing extensive damage to tooth structure. When the damage goes beyond what can be treated with a filling, dentists can perform a root canal (or endodontics), preserving the tooth and retaining its original integrity; thereby, saving a tooth that in the past would have to have been pulled.
This procedure involves:
- The patient undergoes anesthesia.
- A dental dam is used to isolate the tooth.
- The tooth is opened to allow for removal of infected or dead dental pulp.
- The tooth is comprehensively cleaned, including any cracks and canals.
- With special tools, the doctor reshapes the canals.
- The tooth is filled again with cutting edge biocompatible filling material.
- A temporary covering is used to cover the access opening.
- Patients must see their regular dentist quickly for a permanent restoration of the tooth.